Introduction to Vacuum Plating:
Vacuum plating mainly includes vacuum evaporation, sputtering, and ion plating. They are all used to form various metal and non-metal films on the surface of the product by distillation or sputtering under vacuum conditions, so as to achieve the effect of electroplating.
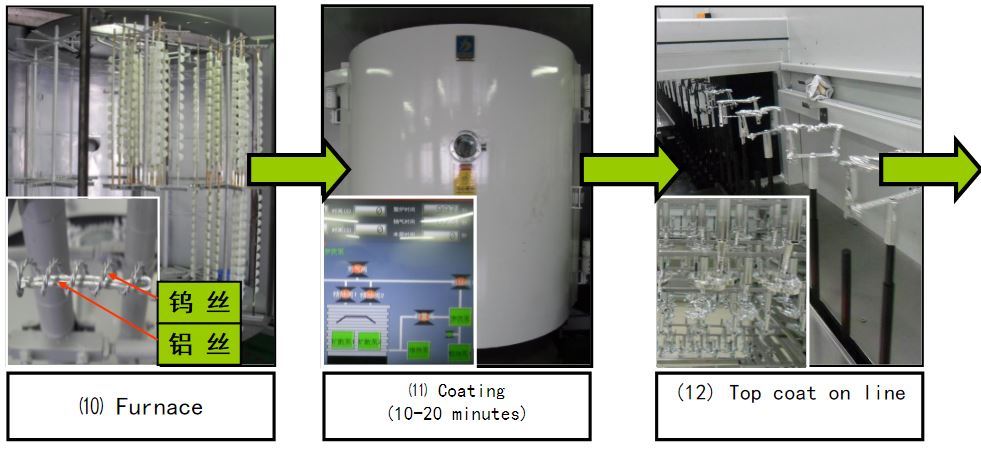
LKKER SCM currently uses mainly vacuum evaporation. Vacuum evaporation (vacuum evaporation coating) is a technology in which the evaporated material is heated by an evaporator to vaporize it under vacuum conditions, and the evaporated particle stream is directly shot to the product and deposited to form a solid film on the product.
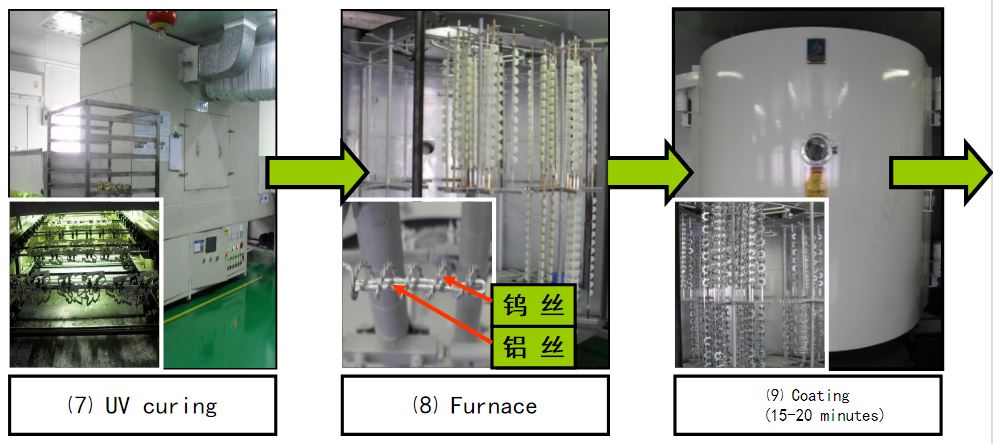
The film material (aluminum wire) is placed in the evaporation source (tungsten wire) in the vacuum chamber. Under high vacuum conditions, the evaporation source heats up to make it evaporate. After the atoms and molecules of the film material vapor escape from the surface of the evaporation source, they are directly When it reaches the surface of the product to be plated, due to the low temperature of the product, it condenses to form a film.
In terms of the production process, LKKER SCM has expanded from a single manual electroplating line in the original Shenzhen Guanlan factory to a vacuum electroplating department integrating automatic and manual lines in the current Tangxia factory.
Introduction to Electroplating process:
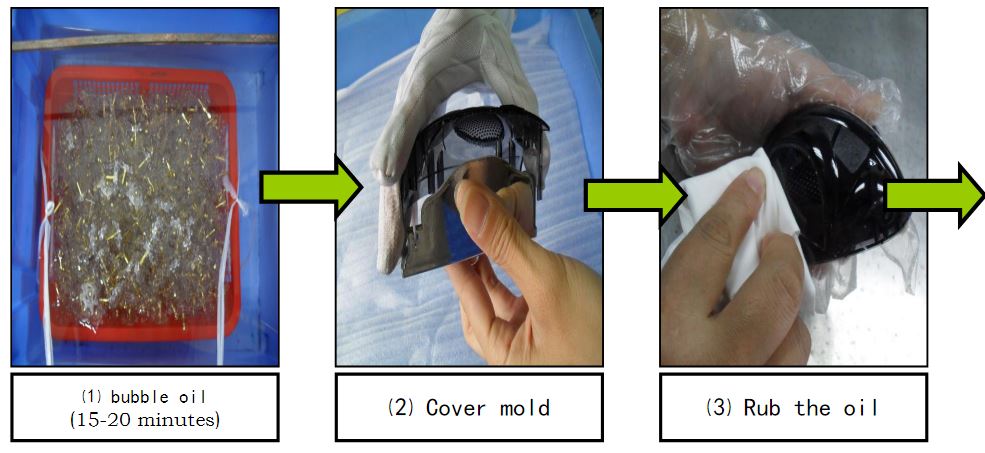
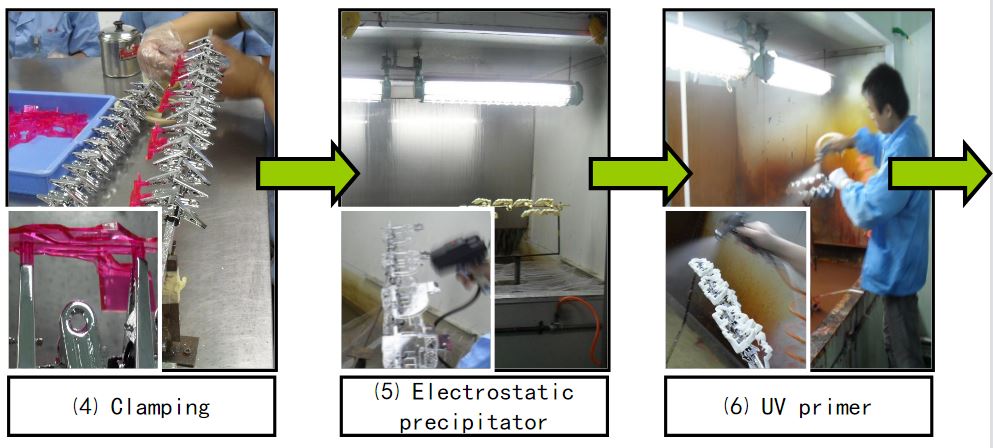
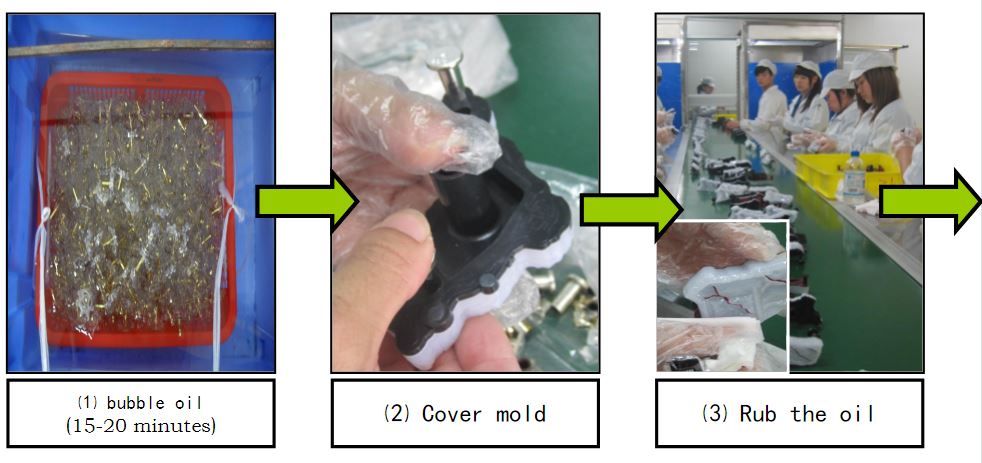
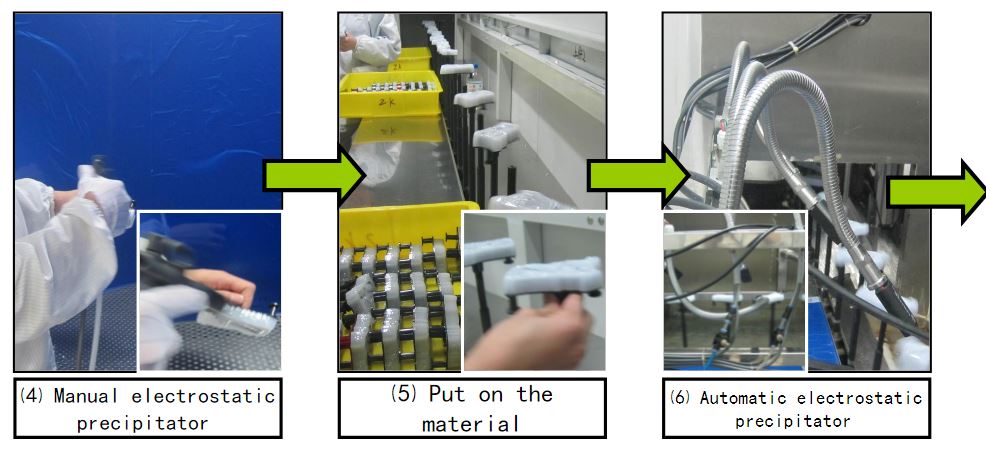
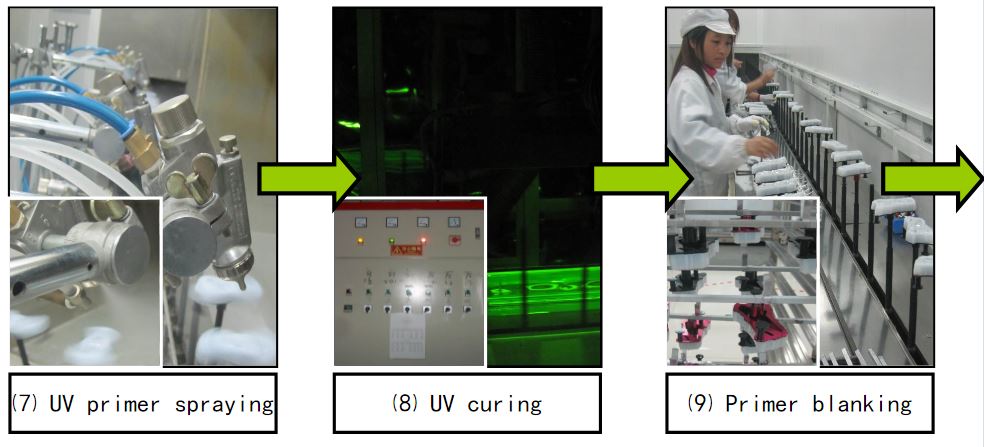
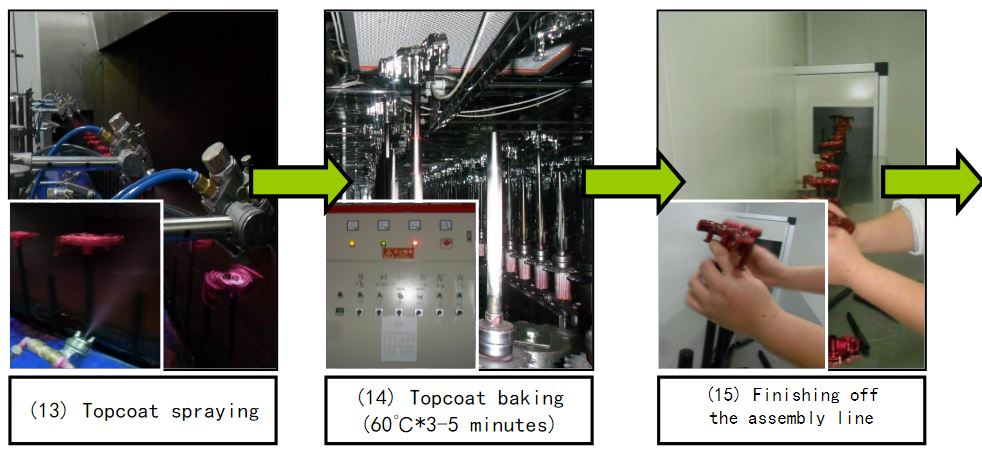
Material degreasing → cover mold → clamping → dust removal → UV spraying
→UV Curing → Coating → Finishing → Baking → Inspection → Packaging
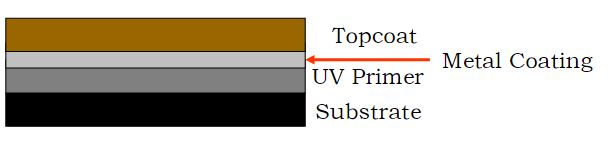
A sketch of the effect of vacuum plating:
Vacuum plating process (1): manual production line process
Vacuum plating process (2): automate production line process
Defective 1. Lines/dust spots
Description: The raised granules or lines on the surface of the product are bad, and the distribution is irregular.
Analysis of the causes:
- The surface of the material is not cleaned or cleaned in place
- Invisible wool (plastic wire) produced at the corners of the product during the molding process
- Too much dust in the air or on the floor
- Dust from the workshop vents
- Flying dust inside the equipment (such as UV machine, etc.)
- Paint pollution or poor paint
- Flying dust or fibers/hair on the human body falls on the product during operation
Key points of quality control:
- When pre-processing materials, confirm whether the operator's dust removal method is in accordance with the requirements of the "Operation Instructions"
- When the materials are received, refer to the standard template and "Inspection Benchmarks" for confirmation
- Regularly confirm the workshop "3S" during the inspection process
- Confirm the use of the ventilation system during the process inspection, and confirm whether the ventilation equipment is regularly inspected and maintained
- Regularly check the equipment maintenance records and "3S" to confirm whether the equipment is regularly inspected and maintained.
- Before using the paint, test spray to confirm, and replace the bad paint in time.
- Check whether the workshop workers wear electrostatic clothes/caps as required Wait
Defective 2. Oil stains/oil spots
Description: The concave shape on the surface of the product is not good, the shape is generally round or oval, and it is diffuse. Neat edges generally appear in the groove position of the product
Analysis of the causes:
- The oil on the surface of the material has not been treated.
- The material itself has too much oil and cannot be removed by normal degreasing.
- There is water or oil in the air pipe of the spray gun. 4. The paint is bad or polluted.
Key points of quality control:
- Confirm whether the operation method is consistent with the "Operation Instructions" during pre-processing
- Regularly confirm the use of mold release agents at the molding site
- Check whether there is water in the spray gun every day before production
- Confirm the paint before production, and deal with the expired paint in time
Defective 3. Explosive tungsten wire
Description: The light transmission of tungsten filaments generally occurs on transparent or translucent PC materials that require cover mold plating. Light is irradiated, and the light passes through the coating position.
Analysis of the causes:
The electroplating tungsten wire is aging, and the undissolved part of the aluminum wire falls on the product after evaporation to form light transmission
Key points of quality control:
Check the appearance of the tungsten wire before going online, if there is obvious nodule or oxidation, it cannot be used, and regularly confirm the replacement record of the tungsten wire
Defective 4. Electroplating pinhole light transmission
Description: Pinhole light transmission generally occurs on PC transparent or translucent materials that require cover mold plating, illuminated with light, and the light passes through the coating position.
Analysis of the causes:
- 1. The electroplating tungsten wire is aging, and the undissolved part of the aluminum wire falls on the product after evaporation to form pinhole-shaped light transmission
- After the primer is cured, flying dust adheres to the surface, resulting in pinhole light transmission after electroplating
- The purity of electroplated aluminum wire is too low and contains impurities
- The thickness of the coating is too thick
- Before the topcoat is sprayed, the dust removal pressure is too high
- The spray pressure of the topcoat is too high
More in the next chapter. Follow LKKER SCM Linkedin Page for chapter updates.
Latest

October 2024
LKK and HHOGene launch world's first light-controlled TWS earbuds
Technical April 2025
LKK Design Wins 8 Red Dot Awards in 2025
Technical March 2025
The Designer Festival was successfully held at LKK Design
News April 2025
LKK Design Ushers in a New Chapter in Shenzhen: Driving Strategic Growth Through Product Design
Technical October 2024
LKK Design participated in the 90th Shenzhen International Medical Exhibition
News October 2024